Open Master's Thesis Positions
On this page you will find a selection of possible Master Thesis opportunities, some notified to us directly by the research groups of MEST Tutors and some listed on the SiROP database.
This list is not exhaustive, other Thesis projects might exist, please check the respective listings of Departments and research groups you are particularly interested in.
See also Internship opportunities.
Master projects:
- external page Vertical Extensions: A Technological-Ecological Analysis through archetyping at the Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
- Download Assessing the innovation potential of electrochemical direct air capture (PDF, 122 KB) at the Energy and Technology Policy Group
Projects from the SiROP Database
ETH Zurich uses SiROP to publish and search scientific projects. Here is a selection of projects currently available which may be suitable for MEST students. For more information visit external page sirop.org.
Iterative Learning Motion and Extrusion Control for Additive Manufacturing Processes
 Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has seen widespread adoption in many engineering fields, including biomedical, aerospace, and automotive applications. Its ability to manufacture complex designs accurately and quickly offers significant advantages in rapid prototyping, customization, and design flexibility for mechanical assembly. As an additive manufacturing technique, fused deposition modeling (FDM) is governed by two key dynamics: motion and extrusion. In FDM, a triple axis system controls the movement of the extrusion head, which melts and deposits plastic filament onto the printing bed. However, these dynamics are inherently coupled, whereby the extrusion width is directly affected by the motion of the system. Given that the printing motion is highly repetitive, it is advantageous to leverage this behavior when designing a control system.
Show details
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has seen widespread adoption in many engineering fields, including biomedical, aerospace, and automotive applications. Its ability to manufacture complex designs accurately and quickly offers significant advantages in rapid prototyping, customization, and design flexibility for mechanical assembly. As an additive manufacturing technique, fused deposition modeling (FDM) is governed by two key dynamics: motion and extrusion. In FDM, a triple axis system controls the movement of the extrusion head, which melts and deposits plastic filament onto the printing bed. However, these dynamics are inherently coupled, whereby the extrusion width is directly affected by the motion of the system. Given that the printing motion is highly repetitive, it is advantageous to leverage this behavior when designing a control system.
Show details
Keywords
Motion control, adaptive control, learning control, robotics
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
Earliest start: 2025-03-31
Applications limited to: ETH Zurich
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Hoteit Rawan , Zuliani Riccardo
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Demand-Side Flexibility Allocation for Buildings: An Optimization-Based Approach
 The increasing integration of distributed renewable energy sources into electric power grids has highlighted the critical need for demand-side energy flexibility to balance intermittent power generation and ensure grid stability. Buildings, as major energy consumers, present a promising source of flexibility by adjusting their energy consumption to support grid requirements while maintaining occupants' thermal comfort. To achieve this, each building must manage its room temperatures to minimize cost while adhering to technical and operational constraints, as well as fulfilling flexibility provisions. Our preliminary studies indicate that reinforcement learning (RL) is a promising control strategy that can effectively meet these objectives \cite{svetozarevic2022data}. However, in practice, aggregators often prefer to provide flexibility targets to groups of buildings rather than to individual units, making direct implementation of RL-based control challenging.
This project aims to develop a mechanism for distributing flexibility provisions from a central system to individual buildings within a designated group. The goal is to allocate flexibility efficiently while maximizing social and economic welfare across all buildings in the category.
Show details
The increasing integration of distributed renewable energy sources into electric power grids has highlighted the critical need for demand-side energy flexibility to balance intermittent power generation and ensure grid stability. Buildings, as major energy consumers, present a promising source of flexibility by adjusting their energy consumption to support grid requirements while maintaining occupants' thermal comfort. To achieve this, each building must manage its room temperatures to minimize cost while adhering to technical and operational constraints, as well as fulfilling flexibility provisions. Our preliminary studies indicate that reinforcement learning (RL) is a promising control strategy that can effectively meet these objectives \cite{svetozarevic2022data}. However, in practice, aggregators often prefer to provide flexibility targets to groups of buildings rather than to individual units, making direct implementation of RL-based control challenging.
This project aims to develop a mechanism for distributing flexibility provisions from a central system to individual buildings within a designated group. The goal is to allocate flexibility efficiently while maximizing social and economic welfare across all buildings in the category.
Show details
Keywords
Building control _ Demand side management - Optimization - Flexibility
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-04-01
Organization: Urban Energy Systems
Hosts: Bellizio Federica , Nortmann Benita , Montazeri Mina
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Feedback Optimization for Freeway Ramp Metering
 Online Feedback optimization (OFO) is a beautiful control method to drive a dynamical system to an
optimal steady-state. By directly interconnecting optimization algorithms with real-time system measurements, OFO guarantees robustness and efficient operation, yet without requiring exact knowledge
of the system model. The goal of this project is to develop faster OFO schemes for congestion control
on freeways, in particular by leveraging the monotonicity properties of traffic networks.
Show details
Online Feedback optimization (OFO) is a beautiful control method to drive a dynamical system to an
optimal steady-state. By directly interconnecting optimization algorithms with real-time system measurements, OFO guarantees robustness and efficient operation, yet without requiring exact knowledge
of the system model. The goal of this project is to develop faster OFO schemes for congestion control
on freeways, in particular by leveraging the monotonicity properties of traffic networks.
Show details
Keywords
Feedback optimization, monotone systems, freeway ramp metering, timescale separation
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-01-15
Latest end: 2025-12-15
Applications limited to: ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , Empa
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Chandrasekaran Sanjay , Bianchi Mattia
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Experimental Testing of Facade Components with Solar Simulator
 As the main interface between interior and exterior environments, facades hold great potential to support the decarbonization of the building sector, while providing high visual and thermal comfort levels. The Solar Simulator and climatic chamber at the Zero Carbon Building Systems Lab [3] offer the opportunity to test and analyze the performance of envelope components, supporting the development of new facade system. After the completion of a first calibration phase, the lab infrastructure shall now be extended to a validated experimental setup for measuring solar gains, heat and light transmission through 1:1 scale facade components. The establishment of testing protocols and their validation is essential to enable the use of the laboratory infrastructure for future research projects. This thesis will develop a validated setup for measuring the angle-dependent solar, optical and thermal exchanges through facade systems.
Show details
As the main interface between interior and exterior environments, facades hold great potential to support the decarbonization of the building sector, while providing high visual and thermal comfort levels. The Solar Simulator and climatic chamber at the Zero Carbon Building Systems Lab [3] offer the opportunity to test and analyze the performance of envelope components, supporting the development of new facade system. After the completion of a first calibration phase, the lab infrastructure shall now be extended to a validated experimental setup for measuring solar gains, heat and light transmission through 1:1 scale facade components. The establishment of testing protocols and their validation is essential to enable the use of the laboratory infrastructure for future research projects. This thesis will develop a validated setup for measuring the angle-dependent solar, optical and thermal exchanges through facade systems.
Show details
Keywords
Building façade, daylighting, thermal performance, solar gains, experimental study
Labels
Master Thesis , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-04-01
Latest end: 2025-10-31
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Piccioni Valeria
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
System Integration and optimization of Wind Energy Potentials in Switzerland
 Integrating wind energy into Switzerland’s future energy system remains a complex challenge, with optimal use of available potential in an integrated system still underexplored. This project aims to enhance wind energy assessments by incorporating spatial-temporal wind potential into energy system modeling and analyzing its role in Switzerland’s energy transition, including social aspects.
Show details
Integrating wind energy into Switzerland’s future energy system remains a complex challenge, with optimal use of available potential in an integrated system still underexplored. This project aims to enhance wind energy assessments by incorporating spatial-temporal wind potential into energy system modeling and analyzing its role in Switzerland’s energy transition, including social aspects.
Show details
Keywords
energy system modelling, system optimisation, wind energy, renewable energy, energy system analysis
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-04-01
Latest end: 2025-12-31
Organization: Urban Energy Systems
Hosts: Chen Yi-Chung
Topics: Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Data-driven Safe Control Design: A Certificate Function Approach
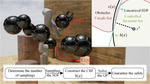 Safety is a fundamental requirement for critical systems such as power converter protection, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. Ensuring long-term safety in these systems requires both characterizing safe behaviour and designing feedback controllers that enforce safety constraints. Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) have recently emerged as a powerful tool for addressing these challenges by defining safe regions in the state space and formulating control strategies that maintain safety. When the dynamical system is precisely modeled, a CBF can be designed by solving a convex optimization problem, where the state-space model is incorporated into the constraints.
However, designing valid CBFs remains difficult when system models are uncertain or time-varying. More importantly, CBFs and control laws derived from inaccurate models may lead to unsafe behaviour in real-world systems. To overcome these difficulties, this project aims to develop a data-driven approach for constructing CBFs without relying on explicit system models. Instead, we will leverage behavioural systems theory to replace model information in the design program by persistently exciting data. The proposed method will be applied to output current protection in power converters or robotics collision avoidance.
Show details
Safety is a fundamental requirement for critical systems such as power converter protection, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. Ensuring long-term safety in these systems requires both characterizing safe behaviour and designing feedback controllers that enforce safety constraints. Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) have recently emerged as a powerful tool for addressing these challenges by defining safe regions in the state space and formulating control strategies that maintain safety. When the dynamical system is precisely modeled, a CBF can be designed by solving a convex optimization problem, where the state-space model is incorporated into the constraints.
However, designing valid CBFs remains difficult when system models are uncertain or time-varying. More importantly, CBFs and control laws derived from inaccurate models may lead to unsafe behaviour in real-world systems. To overcome these difficulties, this project aims to develop a data-driven approach for constructing CBFs without relying on explicit system models. Instead, we will leverage behavioural systems theory to replace model information in the design program by persistently exciting data. The proposed method will be applied to output current protection in power converters or robotics collision avoidance.
Show details
Keywords
Data-driven control, model-free control, optimal control, safety-critical systems
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-03-03
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Wang Han , Moffat Keith , Fochesato Marta
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Vertical Extensions: A Technological-Ecological Analysis through archetyping
 Urban densification in cities like Zurich necessitates sustainable strategies that address environmental, social, and economic priorities. Vertical extensions—adding floors to existing buildings—offer a viable solution to increase housing capacity while minimizing land use and preserving the urban fabric. However, implementation is often hindered by regulatory, technical, and socio-economic challenges. This project focuses on analyzing vertical extensions through an archetyping approach, with an emphasis on identifying key technological and ecological parameters that influence project success. By examining case studies, collecting data, and conducting statistical analyses, the research seeks to uncover correlations between these parameters and project outcomes. The findings aim to inform future sustainable densification strategies and guide decision-making.
Show details
Urban densification in cities like Zurich necessitates sustainable strategies that address environmental, social, and economic priorities. Vertical extensions—adding floors to existing buildings—offer a viable solution to increase housing capacity while minimizing land use and preserving the urban fabric. However, implementation is often hindered by regulatory, technical, and socio-economic challenges. This project focuses on analyzing vertical extensions through an archetyping approach, with an emphasis on identifying key technological and ecological parameters that influence project success. By examining case studies, collecting data, and conducting statistical analyses, the research seeks to uncover correlations between these parameters and project outcomes. The findings aim to inform future sustainable densification strategies and guide decision-making.
Show details
Keywords
Vertical extensions Urban densification Technical-Ecological Analysis Case study analysis Archetyping Construction Methods Structural Engineering Life-cycle assessment (LCA)
Labels
Master Thesis , Master in Integrated Building Systems (ETHZ) , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
Earliest start: 2025-03-01
Latest end: 2025-09-15
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Gester Maximilian
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
Data-Driven Power System Stabilization with Dissipativity-Informed Neural Networks
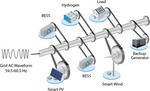 Modern power systems exhibit significant complexity, making their analysis and control particularly challenging, especially when precise system models are unavailable. Traditional model-based control strategies often fail to scale with increasing system complexity, while recent advances in nonlinear, learning based control offer promising alternatives. However, many of these methods lack formal stability guarantees, which are crucial for safety-critical applications such as power system frequency control. This project aims to bridge this gap by developing a deep learning framework for analyzing the dissipativity properties of power systems and designing stabilizing controllers with formal guarantees.
Show details
Modern power systems exhibit significant complexity, making their analysis and control particularly challenging, especially when precise system models are unavailable. Traditional model-based control strategies often fail to scale with increasing system complexity, while recent advances in nonlinear, learning based control offer promising alternatives. However, many of these methods lack formal stability guarantees, which are crucial for safety-critical applications such as power system frequency control. This project aims to bridge this gap by developing a deep learning framework for analyzing the dissipativity properties of power systems and designing stabilizing controllers with formal guarantees.
Show details
Keywords
Deep learning, data-driven control, dissipativity, power systems
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-02-17
Applications limited to: ETH Zurich
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Wang Han , Moffat Keith
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Designing High-Performance MPC Controllers Under Environmental Changes Using Meta-Learning
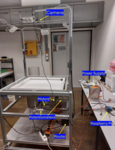 Model predictive control (MPC) is a widely used control technique that optimizes control inputs while fulfilling process constraints. Although automated tuning methods have been developed for task-specific MPC, they struggle when tasks change over time, requiring costly re-tuning. This project aims to reduce the computational burden of re-tuning by leveraging meta-learning, enabling efficient adaptation of controllers to different environments with minimal data.
Show details
Model predictive control (MPC) is a widely used control technique that optimizes control inputs while fulfilling process constraints. Although automated tuning methods have been developed for task-specific MPC, they struggle when tasks change over time, requiring costly re-tuning. This project aims to reduce the computational burden of re-tuning by leveraging meta-learning, enabling efficient adaptation of controllers to different environments with minimal data.
Show details
Keywords
Meta-Learning, Model Predictive Control, Learning-based Control
Labels
Semester Project
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-02-16
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Schmid Niklas
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Optimizing district thermal network design and phasing strategies using the City Energy Analyst
 This research focuses on optimizing district thermal network design and phasing strategies by incorporating existing infrastructure and studying interplays with urban design metrics. While many existing district thermal network models often assume the absence of prior infrastructure, this study introduces methodologies to account for existing pipes, plants, and pumps, enabling a more realistic scenario for network planning. Additionally, the research explores phased implementation strategies to maximize return on investment under budget constraints, providing a pathway for incremental network construction and operation.
A key aspect of the study is the feedback loop between urban design and thermal network engineering, which quantifies how urban parameters such as building density, land use types, and development phasing affect network performance, and vice versa. The proposed methodologies are applied to case studies in Zurich, Singapore, and Shanghai, representing diverse climatic and urban contexts.
The outcomes include a framework for integrating existing infrastructure, strategies for phased implementation, and insights into the dynamic interplay between urban design and district energy systems. If time permits, the research will also produce a computational prototype for integration into the City Energy Analyst (CEA).
Show details
This research focuses on optimizing district thermal network design and phasing strategies by incorporating existing infrastructure and studying interplays with urban design metrics. While many existing district thermal network models often assume the absence of prior infrastructure, this study introduces methodologies to account for existing pipes, plants, and pumps, enabling a more realistic scenario for network planning. Additionally, the research explores phased implementation strategies to maximize return on investment under budget constraints, providing a pathway for incremental network construction and operation.
A key aspect of the study is the feedback loop between urban design and thermal network engineering, which quantifies how urban parameters such as building density, land use types, and development phasing affect network performance, and vice versa. The proposed methodologies are applied to case studies in Zurich, Singapore, and Shanghai, representing diverse climatic and urban contexts.
The outcomes include a framework for integrating existing infrastructure, strategies for phased implementation, and insights into the dynamic interplay between urban design and district energy systems. If time permits, the research will also produce a computational prototype for integration into the City Energy Analyst (CEA).
Show details
Keywords
District thermal network; Urban design; Retrofitting; City Energy Analyst
Labels
Master Thesis , Master in Integrated Building Systems (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-03-03
Latest end: 2025-03-24
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Shi Zhongming
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
Optimizing Urban Form for Energy Efficiency and Environmental Performance: A Comparative Analysis of Grasshopper-CEA Workflow and Alternative Tools
 Urban form plays a critical role in shaping the energy efficiency and environmental sustainability of cities. This study explores the optimization of urban design parameters—such as building geometry, height, layout, and floor area ratio (FAR) - using the Grasshopper-CEA pipeline. The research develops a structured workflow that integrates parametric design in Grasshopper with energy performance simulation in the City Energy Analyst (CEA).
In addition to developing this workflow, the study benchmarks it against alternative tools commonly used for urban design and energy simulation. The comparison evaluates workflows based on usability and computational efficiency, using consistent input parameters and objectives. Results highlight the strengths and limitations of each approach, offering insights into the trade-offs between computational complexity and design performance.
This research provides a replicable framework for urban planners and architects to optimize urban forms for energy and environmental objectives. It also offers a critical perspective on the tools available for parametric urban design, guiding future tool development and integration strategies.
Show details
Urban form plays a critical role in shaping the energy efficiency and environmental sustainability of cities. This study explores the optimization of urban design parameters—such as building geometry, height, layout, and floor area ratio (FAR) - using the Grasshopper-CEA pipeline. The research develops a structured workflow that integrates parametric design in Grasshopper with energy performance simulation in the City Energy Analyst (CEA).
In addition to developing this workflow, the study benchmarks it against alternative tools commonly used for urban design and energy simulation. The comparison evaluates workflows based on usability and computational efficiency, using consistent input parameters and objectives. Results highlight the strengths and limitations of each approach, offering insights into the trade-offs between computational complexity and design performance.
This research provides a replicable framework for urban planners and architects to optimize urban forms for energy and environmental objectives. It also offers a critical perspective on the tools available for parametric urban design, guiding future tool development and integration strategies.
Show details
Keywords
Urban form optimization, grasshopper, parametric design
Labels
Semester Project , Master in Integrated Building Systems (ETHZ)
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
Earliest start: 2025-03-03
Latest end: 2025-03-24
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Shi Zhongming
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
INVESTIGATION OF ENERGY SAVINGS POTENTIAL OF SOLAR THERMAL COLLECTORS INTEGRATED WITHIN ETICS (EXTERNAL THERMAL INSULATION COMPOSITE SYSTEM) FACADES.
 The construction industry accounts for approximately 40% of global CO2 emissions, primarily from operational energy demands such as heating, cooling, and powering buildings. Over 60% of Europe's household energy consumption is dedicated to heating, making reducing CO2 emissions from residential heating essential to achieving sustainability goals. A combination of strategies is key to increasing sustainability: reducing heating demand through effective insulation and utilizing renewable energy sources.
External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) provide cost-effective insulation for building envelopes, while heat pumps offer a sustainable heating solution by leveraging environmental heat. However, urban environments often lack the space needed for traditional heat pump components, creating a demand for innovative solutions.
External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) represent one of Switzerland's most common facade types. The system, shown in Figure 1, typically consists of several layers: an adhesive or bonding layer (1), insulation material such as EPS or mineral wool (2), additional fasteners (3), a base render coat (4) including glass-fibre reinforcement (5), a finishing render coat (6), and optionally a paint layer.
This thesis explores the integration of solar thermal collectors into ETICS facades as a novel approach to enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational emissions in buildings. The thesis will contribute to developing functional facades that reduce energy consumption and operational emissions, supporting the global transition to sustainable building technologies.
Show details
The construction industry accounts for approximately 40% of global CO2 emissions, primarily from operational energy demands such as heating, cooling, and powering buildings. Over 60% of Europe's household energy consumption is dedicated to heating, making reducing CO2 emissions from residential heating essential to achieving sustainability goals. A combination of strategies is key to increasing sustainability: reducing heating demand through effective insulation and utilizing renewable energy sources.
External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) provide cost-effective insulation for building envelopes, while heat pumps offer a sustainable heating solution by leveraging environmental heat. However, urban environments often lack the space needed for traditional heat pump components, creating a demand for innovative solutions.
External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) represent one of Switzerland's most common facade types. The system, shown in Figure 1, typically consists of several layers: an adhesive or bonding layer (1), insulation material such as EPS or mineral wool (2), additional fasteners (3), a base render coat (4) including glass-fibre reinforcement (5), a finishing render coat (6), and optionally a paint layer.
This thesis explores the integration of solar thermal collectors into ETICS facades as a novel approach to enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational emissions in buildings. The thesis will contribute to developing functional facades that reduce energy consumption and operational emissions, supporting the global transition to sustainable building technologies.
Show details
Keywords
Solar thermal collector, ETICS, render, functional facades, prototyping, simulation
Labels
Master in Integrated Building Systems (ETHZ)
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
Earliest start: 2025-03-03
Latest end: 2025-09-01
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Crosby Sarah
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
Structural Testing of 3D-printed Polymer Materials for Sustainable Façade Systems
 Large-scale polymer 3D printing offers unique geometric freedom and performance integration, enabling the creation of lightweight, sustainable, and functional facade systems. Within the existing research efforts of NCCR DFAB, this project focuses specifically on mechanical testing to compare different polymer materials for use in 3D-printed facade systems. The research evaluates mechanical properties such as bending, impact, and tensile strength to determine the most suitable materials for lightweight facade components. Comparisons are made based on how the materials meet mechanical performance requirements for functional facades.
Show details
Large-scale polymer 3D printing offers unique geometric freedom and performance integration, enabling the creation of lightweight, sustainable, and functional facade systems. Within the existing research efforts of NCCR DFAB, this project focuses specifically on mechanical testing to compare different polymer materials for use in 3D-printed facade systems. The research evaluates mechanical properties such as bending, impact, and tensile strength to determine the most suitable materials for lightweight facade components. Comparisons are made based on how the materials meet mechanical performance requirements for functional facades.
Show details
Keywords
3D printing, facade design, polymer materials, mechanical testing
Labels
Semester Project , Master in Integrated Building Systems (ETHZ) , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-03-24
Latest end: 2025-06-02
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Piccioni Valeria
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
Predictive Modeling for Energy Consumption and Emissions in Robotic 3D Printing
Digital and robotic fabrication techniques are increasingly being explored to create building components with embedded functionalities, offering unparalleled opportunities for customization.
As the adoption of robotic 3D printing grows, it becomes crucial to evaluate the environmental impacts of these processes, particularly their energy consumption and associated emissions. Understanding these impacts is essential to assess the sustainability of robotic 3D printing processes.
This project, enabled by real-world data provided by Saeki Robotics, aims to develop a predictive model to assess and forecast energy consumption and emissions in robotic 3D printing.
Show details
Keywords
robotic 3D printing, energy, and emissions, machine learning, additive manufacturing
Labels
Semester Project , Master in Integrated Building Systems (ETHZ) , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-03-23
Latest end: 2025-06-02
Organization: Chair of Architecture and Building Systems
Hosts: Piccioni Valeria
Topics: Architecture, Urban Environment and Building
Details: Open this project...
System theory of iterative methods
 Modern control methods often rely on explicit online computation. In order to understand such closed loops between numerical methods and dynamical systems, this project
approaches the algorithm as a dynamical system itself. In doing so, the usual
language of convergence of algorithms can be viewed as a special case of stability
theory.
Show details
Modern control methods often rely on explicit online computation. In order to understand such closed loops between numerical methods and dynamical systems, this project
approaches the algorithm as a dynamical system itself. In doing so, the usual
language of convergence of algorithms can be viewed as a special case of stability
theory.
Show details
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Eising Jaap
Topics: Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Identifying influencers in social networks
 The objective of this project is the design and analysis of recommender systems as optimization algorithms representing a robust feedback controller. We aim to design recommender system algorithms that identify influential users using observable data from users (for example: clicks/ time spent on a page/ likes etc.) in a social network and provide recommendations accordingly.
Show details
The objective of this project is the design and analysis of recommender systems as optimization algorithms representing a robust feedback controller. We aim to design recommender system algorithms that identify influential users using observable data from users (for example: clicks/ time spent on a page/ likes etc.) in a social network and provide recommendations accordingly.
Show details
Keywords
Control theory, online feedback optimization, social networks, opinion dynamics, Kalman filtering, recommender systems
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2025-02-17
Latest end: 2025-12-15
Applications limited to: EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , ETH Zurich
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Chandrasekaran Sanjay
Topics: Mathematical Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Experimental Validation of an Impedance Identification Method for Three-Phase Power Systems
 This project aims to use two converter emulators available in the Automatic Control Laboratory of ETHz to experimentally validate a new impedance estimation approach. The main goals are to replicate realistic converter/grid conditions, assess the accuracy and robustness of the estimation method, and to explore its limitations and performance boundaries.
Show details
This project aims to use two converter emulators available in the Automatic Control Laboratory of ETHz to experimentally validate a new impedance estimation approach. The main goals are to replicate realistic converter/grid conditions, assess the accuracy and robustness of the estimation method, and to explore its limitations and performance boundaries.
Show details
Keywords
Impedance Estimation; Grid-connected converters; Power electronics; System Identification
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2024-11-17
Applications limited to: ETH Zurich
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: Abdalmoaty Mohamed , He Xiuqiang
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...
Optimal Excitation for Grid Impedance Estimation
 This project aims to develop optimal excitation schemes for impedance estimation of grid/grid-connected converters.
Show details
This project aims to develop optimal excitation schemes for impedance estimation of grid/grid-connected converters.
Show details
Keywords
Impedance estimation; grid-connected converters; optimal excitation; experiment design; system identification
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Earliest start: 2024-11-17
Applications limited to: ETH Zurich
Organization: Automatic Control Laboratory
Hosts: He Xiuqiang , Abdalmoaty Mohamed
Topics: Engineering and Technology
Details: Open this project...